About topic
Know About topic
Producer Consumer Problem
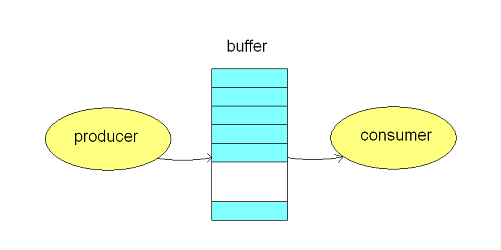
Producer Consumer Problem
Producer Consumer Problem
- The producer should produce data only when the buffer is not full. In case it is found that the buffer is full, the producer is not allowed to store any data into the memory buffer.
- Data can only be consumed by the consumer if and only if the memory buffer is not empty. In case it is found that the buffer is empty, the consumer is not allowed to use any data from the memory buffer.
- Accessing memory buffer should not be allowed to producer and consumer at the same time.
F.A.Q
Frequently Asked Questions
We will be updating the rest of the questions soon
-
What is bounded and unbounded buffer ?
A bounded buffer lets multiple producers and multiple consumers share a single buffer. Producers write data to the buffer and consumers read data from the buffer. Producers must block if the buffer is full.
In unbounded buffer producer is free to add an item into the buffer at any time: it performs wait(mutex) before appending and signal(mutex) afterwards to prevent access by the consumer. It also performs signal(number) after each append to increment number.
-
How can one solve producer Consumer problem ?
Producer consumer problem is a classical synchronization problem. We can solve this problem by using semaphores. A semaphore S is an integer variable that can be accessed only through two standard operations : wait() and signal().
